この記事は金沢工業大学 ロボティクス学科で2021年後学期開講中のロボットプログラミングⅡ用です.
SpeechRecognitionというPythonの音声認識ライブラリはご存知でしょうか。CMU Sphinx、Google Speech Recognition、Google Cloud Speech API、Wit.aiなどのエンジンを使え、エンジンによっては日本語も扱えます。詳細は次のリンクをご覧ください。
今回は、このライブラリを使ったROS2パッケージを作ります。望む機能を実現するROS2パッケージがなくても、それを実現するために便利なライブラリさえあれば自分でROS2パッケージを作ればよいわけです。
方法は今まで学んできたROS2パッケージの作り方と同じで、出力用のパブリッシャと入力用のサブスクライバを作るだけです。
作業環境
- Ubuntu20.02
- ROS2 Foxy
SpeechRecognitionのインストール
- 端末を開いて依存関係のあるものをインストールする。
$ sudo apt install python-dev$ sudo apt install libasound-dev portaudio19-dev libportaudio2 libportaudiocpp0$ pip install pyaudio
- SpeechRecognitionをインストールする。
$ pip install SpeechRecognition
SpeechRecognitionのテスト
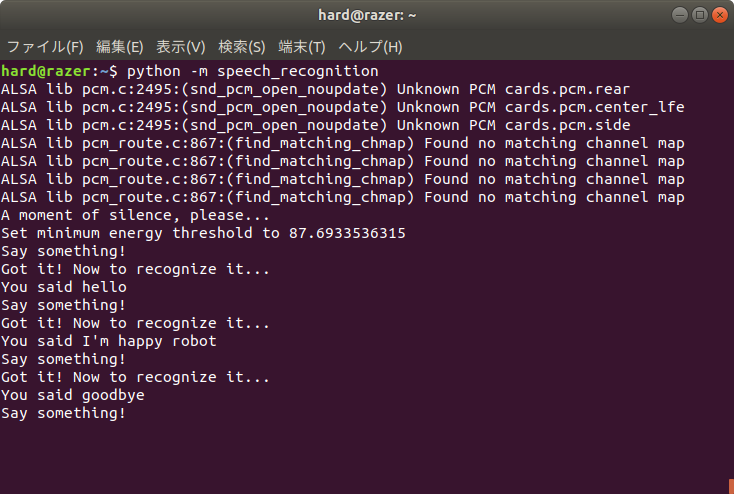
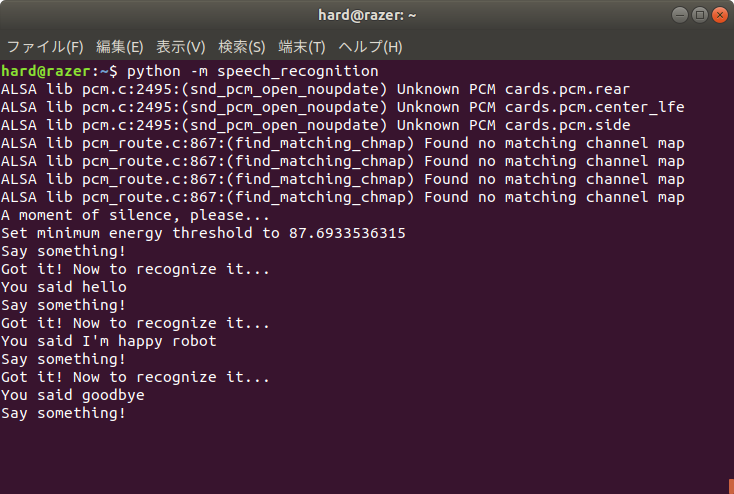
- 端末を開いて、次のコマンドでSpeechRecognitionを実行する。
$ python3 -m speech_recognition
- デフォルトは英語の認識なのでマイクに向かって英語で何か話す。認識されると次のように”You said”の後に認識結果が表示される。
Pythonのサンプルプログラム
- 次に、上で実行したPythonのプログラムを見ていきましょう。まず、ソースコードを入手します。
$ cd ~/src$ git clone https://github.com/Uberi/speech_recognition.git- このプログラムは次のファイルです。
- ~/src/speech_recognition/speech_recognition/__main__.py
- ソースコードsample.pyを表示します。
import speech_recognition as sr # speech_recognitionモジュールにsrという名前を付ける.
r = sr.Recognizer() # Recognizerクラスのインスタンスを生成
m = sr.Microphone() # Microphoneクラスのインスタンスを生成
try:
print("A moment of silence, please...")
# with文.マイクの終了処理を自動でやってくれる.
with m as source:
r.adjust_for_ambient_noise(source)
print("Set minimum energy threshold to {}".format(r.energy_threshold))
while True:
print("Say something!")
with m as source:
audio = r.listen(source)
print("Got it! Now to recognize it...")
try: # 例外処理
# recognize speech using Google Speech Recognition
value = r.recognize_google(audio)
# we need some special handling here to correctly print unicode characters to standard output
if str is bytes: # this version of Python uses bytes for strings (Python 2)
print(u"You said {}".format(value).encode("utf-8"))
else: # this version of Python uses unicode for strings (Python 3+)
print("You said {}".format(value))
except sr.UnknownValueError:
print("Oops! Didn't catch that")
except sr.RequestError as e:
print("Uh oh! Couldn't request results from Google Speech Recognition service; {0}".format(e))
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Ctrl+Cが入力された場合
pass # 何も処理をしない.Pythonのインデントのため必要.
ROSパッケージ化
- では、このプログラムをROSパッケージ化しましょう。トピック通信の場合は大雑把にいうと次の4つを加えるだけです。
- ヘッダ
- ノード
- パブリッシャ
- サブスクライバとそのコールバック関数
- その他
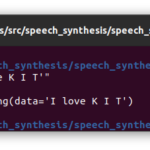
- ROS化したソースコードspeech_recog.pyはこれになります!
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import rclpy # 1.ROS2化:ヘッダ
from rclpy.node import Node # 1.ROS2化:ヘッダ
import speech_recognition as sr
from std_msgs.msg import String
def main():
r = sr.Recognizer()
m = sr.Microphone()
rclpy.init() # 2. ROS2化:ノード
node = Node("speech_recog") # 2. ROS2化:ノード
# 3. ROS2化:パブリッシャ
result_pub = node.create_publisher(String, "/speech_recog_result", 10)
try:
print("A moment of silence, please...")
with m as source:
r.adjust_for_ambient_noise(source)
print("Set minimum energy threshold to {}".format(r.energy_threshold))
while rclpy.ok(): # 5. ROS2化:その他
print("Say something!")
msg = String() # String型のインスタンス生成
with m as source: audio = r.listen(source)
print("Got it! Now to recognize it...")
try:
# recognize speech using Google Speech Recognition
value = r.recognize_google(audio)
msg.data = value
print("You said3: {}".format(value))
result_pub.publish(msg) # 3. ROS2化:パブリッシャ関連
except sr.UnknownValueError:
print("Oops! Didn't catch that")
except sr.RequestError as e:
print("Uh oh! Couldn't request results from Google Speech Recognition service; {0}".format(e))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
rclpy.shutdown() # ROS2化。終了処理。
if __name__ == '__main()__': # このコードをモジュールとしてimport可能にする。ROS2推奨の書き方。
main() # setup.pyのエントリーポイント
ハンズオン:マイクがうまく認識されない,あるいはマイクがない学生は,他のアプリやスマートフォンなどで音声ファイルを作成してから,それを読み込む方法でハンズオンを実行してください.音声ファイルを読み込むSpeech Recognitionは次のリンクをご覧ください.
- sample.pyを実行してみよう!試しに次のスティーブン・ジョブズのスタンフォード大学卒業生に向けた有名なスピーチの以下に示す最後の部分を自分で発話して認識させてみましょう。
“Stay Hungry. Stay Foolish.” It was their farewell message as they signed off. Stay Hungry. Stay Foolish. And I have always wished that for myself. And now, as you graduate to begin anew, I wish that for you.
- speech_recog.pyを使ったspeech_recogパッケージを作り、実行して動作を確認しよう!
- SpeechRecognitionのサンプルプログラムをROS2化しました.ROS2のPythonではクラス化して,音声認識の処理などは,タイマーで呼び出す書き方が多く見られます.SpeechRecognitionクラスを作り,音声処理をするrecognitionメソッドをタイマーで呼び出すようにサンプルプログラムを書き換えてください.
- RoboCupなどの競技会では大会主催者はWiFi環境を準備していますが、通信の品質が悪い場合があります。そのため、オフラインでも音声認識できることが望まれます。SpeechRecognitionライブラリは、音声認識エンジンとしてオフライン用のCMU Sphinxも使えます。ただし、pocket sphinxのインストールが必要です。動作を確認しよう!
終わり
コメント