ROS演習4の知識を使いRoombaをプログラムで動かします。この演習6は演習7を問題を解くためのヒントとなっています。
まず、Robotクラスを作成し、次のメンバ関数を作成します。
- 指定速度[m/s]で指定時間[s]だけ直進して停止するメンバ関数
- void moveForSecond(double linear_vel, double second);
- 指定速度[m/s]で指定の距離[m]だけ直進して停止する以メンバ関数
- void Robot::moveToDistance(double linear_vel, double dist);
// my_robot.cpp
#include "ros/ros.h" // rosで必要はヘッダーファイル
#include <geometry_msgs/Twist.h> // ロボットを動かすために必要
#include <nav_msgs/Odometry.h>
#include <tf/transform_broadcaster.h>
#include <tf/transform_datatypes.h>
#include "unistd.h"
using namespace std;
struct Pose {
double x; // x座標[m] 進行方向
double y; // y座標[m]
double theta; // 姿勢 [rad]
};
class Robot {
private:
Pose pos; // 位置と姿勢
geometry_msgs::Twist vel; // 速度
ros::NodeHandle nh; // ノードハンドラ
ros::Publisher pub; // パブリッシャ
ros::Subscriber sub_odom; //, sub_vel; // サブスクライバ
public:
Robot();
void setLinearVel(double linear_vel); // 並進速度の設定
void setAngularVel(double angular_vel); // 回転速度の設定
void setVel(double linear_vel, double angular_vel);
void odomCallBack(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& msg);
void moveForSecond(double linear_vel, double s); // 指定速度と時間で移動
void moveForSecond2(double linear_vel, double s); // 指定速度と時間で移動
void moveToDistance(double linear_vel, double dist); // 指定速度で指定距離を移動
};
Robot::Robot() {
pub = nh.advertise("/create1/cmd_vel", 10,this);
sub_odom = nh.subscribe("/create1/odom", 100, &Robot::odomCallBack, this);
vel.linear.x = vel.linear.y =vel.linear.z = 0.0; // 並進速度の初期化
vel.angular.z = vel.angular.y = vel.angular.x = 0.0; // 回転速度の初期化
}
// 並進速度の設定
void Robot::setLinearVel(double linear_vel) {
vel.linear.x = linear_vel;
pub.publish(vel);
}
// 回転速度の設定
void Robot::setAngularVel(double angular_vel) {
vel.angular.z = angular_vel;
pub.publish(vel);
}
void Robot::setVel(double linear_vel, double angular_vel = 0) {
vel.linear.x = linear_vel;
vel.angular.z = angular_vel;
pub.publish(vel);
}
// /odomトピックから位置と姿勢、速度を表示
void Robot::odomCallBack(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& msg) {
//ROS_INFO("Seq: %d", msg->header.seq);
//ROS_INFO("/odom Pos (x:%f, y:%f, z:%f)", msg->pose.pose.position.x,msg->pose.pose.position.y, msg->pose.pose.position.z);
pos.x = msg->pose.pose.position.x;
pos.y = msg->pose.pose.position.y;
tf::Quaternion q(msg->pose.pose.orientation.x, msg->pose.pose.orientation.y, msg->pose.pose.orientation.z, msg->pose.pose.orientation.w);
tf::Matrix3x3 m(q);
double roll, pitch, yaw;
m.getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
pos.theta = yaw;
//ROS_INFO("/odom Pose (roll:%f, pitch:%f, yaw:%f) ", roll, pitch, yaw);
//ROS_INFO("Vel (Linear:%f, Angular:%f)", msg->twist.twist.linear.x,msg->twist.twist.angular.z);
}
void Robot::moveForSecond(double linear_vel, double s)
{
setVel(linear_vel); // 指定速度で進む
ros::Duration(s).sleep(); // s秒間スリープ
setVel(0); // 停止
}
void Robot::moveForSecond2(double linear_vel, double s)
{
static ros::Time begin = ros::Time::now();
static int step = 0;
ros::Duration diff(0,0); // diff.sec = diff.nsec = 0と同じ
setVel(linear_vel);
ros::Rate rate(50); // ループの頻度を設定
rate.sleep();
while (diff < ros::Duration(s)) {
ros::spinOnce();
if (step++ == 0) begin = ros::Time::now();
diff = ros::Time::now() - begin;
ROS_INFO("ROS diff: %u.%u",diff.sec,diff.nsec);
rate.sleep();
}
setVel(0);
}
void Robot::moveToDistance(double linear_vel, double dist)
{
double d = 0;
Pose init_pos = pos;
setVel(linear_vel);
ros::Rate rate(50); // ループの頻度を設定
while (d < dist) {
ros::spinOnce();
d = sqrt((pos.x - init_pos.x) * (pos.x - init_pos.x)
+ (pos.y - init_pos.y) * (pos.y - init_pos.y));
ROS_INFO("distance=%.3f[m]",d);
rate.sleep();
}
setVel(0);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "my_robot");
// ros::init()の前にノードハンドラーを生成するとエラーになるので、
// クラス化した場合はオブジェクトの生成はinitの後で行うこと。
Robot robot;
double v = 0.2; // 速度[m/s]
double t = 5.0; // 時間[s]
ROS_INFO("moveSecond:begin");
robot.moveForSecond2(v, t); // 指定した速度と時間で進む
ROS_INFO("moveSecond:end");
ros::Duration(3).sleep(); // 3秒間停止
double d = 3.0; // 距離[m]
ROS_INFO("moveToDistance:begin");
robot.moveToDistance(v, d); // 指定した速度で指定距離を進む
ROS_INFO("moveToDistance:end");
return 0;
}
- 以下ファイルをダウンロードして~/catkin_ws/srcの下にコピーする。
- ホームディレクトリのsrcディレクトリを作成し、移動する。
$ mkdir ~/src$ cd ~/src
- ダウンロードする。
- 学内
$ git clone https://github.com/demulab/robot_programming2.git
- 学外
$ git clone https://github.com/demulab/robot_programming2.git -c http.proxy=""
- 学内
- ~/catkin_ws/srcの下にコピーする。
$ cp -r ~/src/robot_programming2/my_robot ~/catkin_ws/src/.
- ホームディレクトリのsrcディレクトリを作成し、移動する。
- ビルドする
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src$ tar xvf my_robot.tar$ cd ~/catkin_ws$ catkin build my_robot
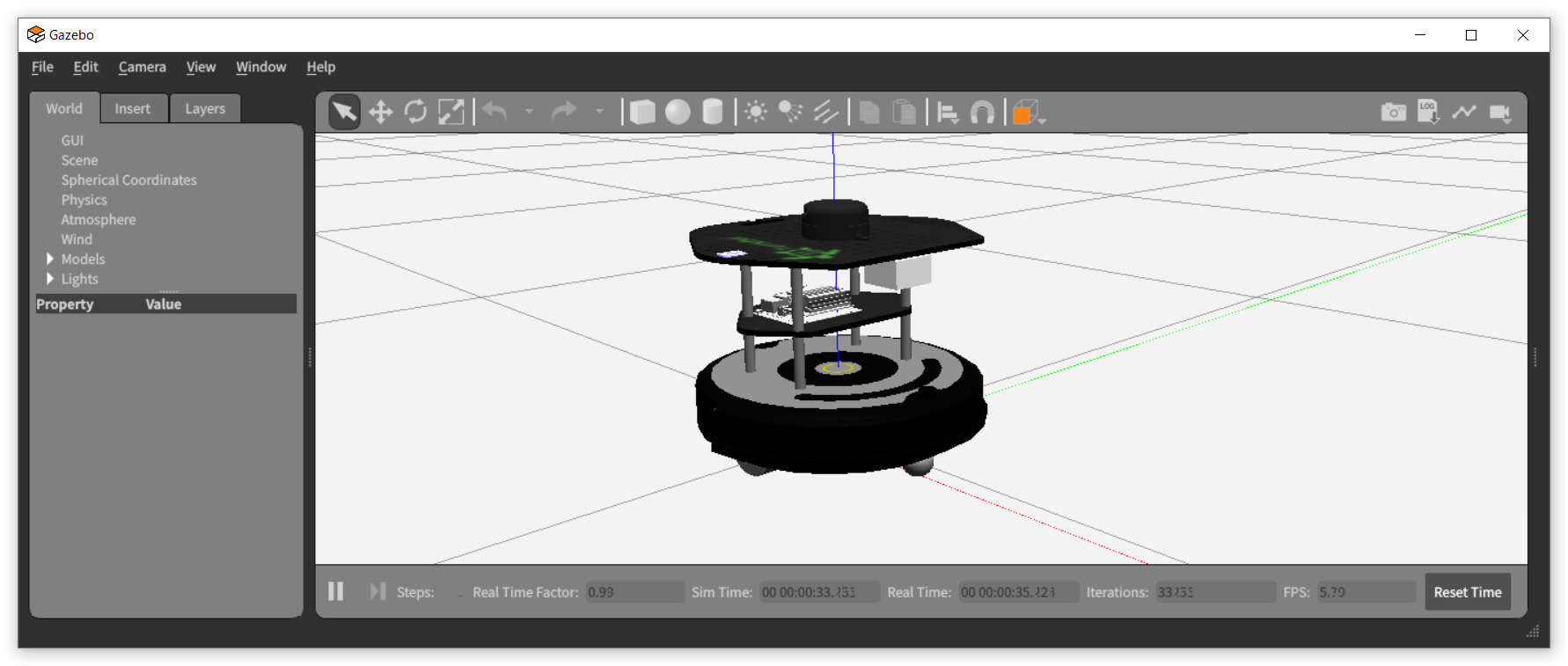
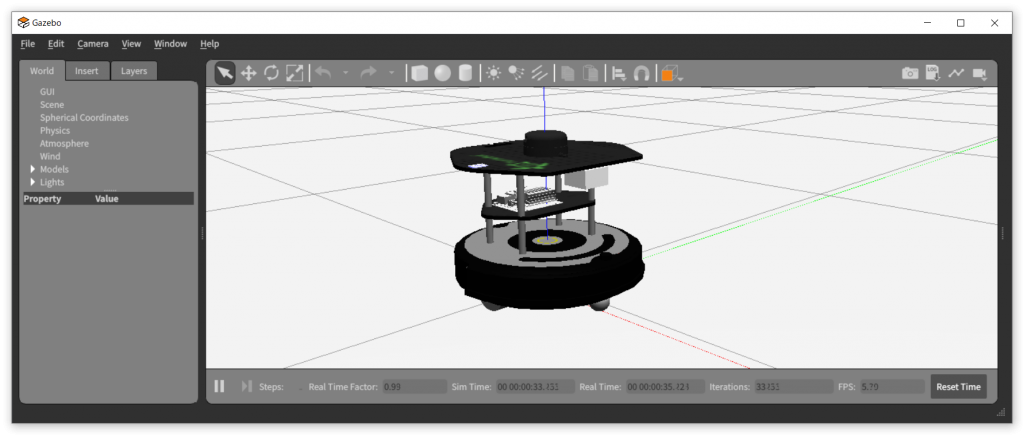
- gazeboでの実行
- 端末を2つ開き、各端末で以下のコマンドを実行する。
$ roslaunch ca_gazebo create_empty_world.launch$ rosrun my_robot my_robot- 実行すると速度0.2[m/s]で5秒間直進し、3秒停止、速度0.2[m/s]で3[m]直進して停止する。

演 習
- 準備
- 以下のROS C++スタイルガイドを参考にRobotクラスを作ろう。
- 基本動作
- Roombaを指定速度[m/s]で直進する以下のメンバ関数を作ろう。
- void Robot::moveAtSpeed(double linear_vel)
- Roombaを指定角速度[rad/s]で回転する以下のメンバ関数を作ろう。
- void Robot::turnAtSpeed(double ang_vel)
- Roombaを指定速度[m/s]で指定の距離[m]だけ直進して停止する以下のメンバ関数を作ろう。
- void Robot::moveToDistance(double linear_vel, double dist)
- Roombaを指定角速度[°/s]で指定の角度[°]だけ回転して停止する以下のメンバ関数を作ろう。
- void Robot::turnToAngle(double ang_vel, double angle)
- Roombaを指定位置(ロボット座標系)へ移動する以下のメンバ関数を作ろう。なお、ROSの座標系なのでロボットの進行方向がx、左方向がy軸の正方向です。
- void Robot::moveToPoint(double x, double y)
- Roombaを指定速度[m/s]で直進する以下のメンバ関数を作ろう。
終わり。お疲れ様!
コメント