今回はROSの通信のもう一つの通信方式であるサービスを理解しましょう。次のROS Wikiを参考にしています。
サービスはROSの通信方法の一つで、双方向通信に使います。ある仕事をお願いするクライアントとそれを処理して返すサーバーからなります。今回、作成するプログラムは速度指令値を送るクライアントと、それをロボットへ伝え(リクエスト)、ロボットから現在の速度を取得しクライアントに返す(レスポンス)サーバーです。次の手順でやりましょう。この例は、前回学んだトピック通信も入れていますので、実践的な内容です。
1.my_serviceパッケージの作成
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src$ catkin_create_pkg my_service std_msgs rospy roscpp
2.srvファイルの作成
srvファイルはやり取りするデータの型を表すテキストファイル。拡張子がsrv、この例のファイル名はWheel.srv。
$ cd ~/catkin_ws/src/my_service$ mkdir srv$ cd srv$ gedit Wheel.srv
内容は次のコード。——-の上が入力(リクエスト)、下が出力(レスポンス)のデータ型を表します。
float64 target_linear_velocity float64 target_angular_velocity --------------- float64 current_linear_velocity float64 current_angular_velocity
サーバーは並進、回転速度指令値target_linear_velocity, target_angular_velocityがリクエストされると、
現在の並進、回転速度current_linear_velocity, current_angular_velocityをリスポンスします。
3.Package.xmlの変更
~/catkin_ws/src/my_service/package.xmlの40、46行目のコメントタグを次のように外す。 つまり、message_generation, message_runtimeを有効にする必要があります。
<!-- Use build_depend for packages you need at compile time: --> <build_depend>message_generation</build_depend> <!-- Use build_export_depend for packages you need in order to build against this package: --> <!-- <build_export_depend>message_generation</build_export_depend> --> <!-- Use buildtool_depend for build tool packages: --> <!-- <buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend> --> <!-- Use exec_depend for packages you need at runtime: --> <exec_depend>message_runtime</exec_depend> <!-- Use test_depend for packages you need only for testing: -->
4.CMakeLists.txtの変更
~/catkin_ws/src/my_service/CMakeLists.txtの13行目、std_msgsの下に次のようにmessage_generationを追加。
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS roscpp rospy std_msgs message_generation )
次の58~62行目を
## Generate services in the 'srv' folder # add_service_files( # FILES # Service1.srv # Service2.srv # )
以下に変更。
## Generate services in the 'srv' folder add_service_files( FILES Wheel.srv )
次の71~74行目
## Generate added messages and services with any dependencies listed here # generate_messages( # DEPENDENCIES # std_msgs # )
のコメントを外し、次にする。
## Generate added messages and services with any dependencies listed here generate_messages( DEPENDENCIES std_msgs )
次に示す105~110行目
#catkin_package( # INCLUDE_DIRS include # LIBRARIES my_service # CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp rospy std_msgs # DEPENDS system_lib #)
を次に変更する。
catkin_package( INCLUDE_DIRS include LIBRARIES my_service CATKIN_DEPENDS roscpp rospy std_msgs message_runtime DEPENDS system_lib )
5.ビルド
ソースコードを書く前にサービスのライブラリを作成するためにcatkin_makeしてビルドしなければなりません。
$ cd ~/catkin_ws$ catkin build
ビルド時にエラーがでたら、CMakelists.txtを変更したか確認し、直して再度ビルド。
6.サービスサーバーのソースコード作成
では、依頼された仕事を処理するサーバープログラムを作ります。次のプログラムをgeditなどを使いwheel_server.cppというファイル名を付けて~/catkin_ws/src/my_service/src/wheel_server.cppと保存。一字でも打ち間違えると動かないのでコピペする。
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include <geometry_msgs/Twist.h>
#include "nav_msgs/Odometry.h"
#include "my_service/Wheel.h" // 自動的に作られる
class Server {
public:
Server(); // コンストラクタ
~Server() {}; // デストラクタ
// オドメトリのコールバック関数
void odomCallback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odom);
// サーバーのコールバック関数(サービスの本体)
bool wheelService(my_service::Wheel::Request &req,
my_service::Wheel::Response &res);
void loop(); // ループ関数
private:
ros::Publisher cmd_pub; // パブリッシャ
ros::Subscriber odom_sub; // サブスクライバ
ros::NodeHandle nh; // ノードハンドルの宣言
ros::ServiceServer service; // サービス
double tmp_linear_velocity; // 現在の並進速度
double tmp_angluar_velocity; // 現在の回転速度
const double max_linear_velocity = 0.7; // 最大並進速度
const double min_linear_velocity = -0.7; // 最小並進速度
const double max_angular_velocity = 1.2; // 最大回転速度
const double min_angular_velocity = -1.2; // 最小回転速度
geometry_msgs::Twist target_vel, tmp_vel; // 目標速度、現在の速度
};
// コンストラクタ
Server::Server()
{
ROS_INFO("Ready to wheel");
//サービスの設定
service = nh.advertiseService("wheel",&Server::wheelService,this);
// パブリッシャ(配信)の設定:
cmd_pub= nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::Twist>("/create1/cmd_vel", 10);
// サブスクライバ(購読)の設定
// /odomトピックはロボットの速度情報を持っている
odom_sub = nh.subscribe("/odom", 10, &Server::odomCallback, this);
// 速度の初期化
target_vel.linear.x = 0.0;
target_vel.linear.y = 0.0;
target_vel.linear.z = 0.0;
target_vel.angular.x = 0.0;
target_vel.angular.y = 0.0;
target_vel.angular.z = 0.0;
tmp_vel.linear.x = 0.0;
tmp_vel.linear.y = 0.0;
tmp_vel.linear.z = 0.0;
tmp_vel.angular.x = 0.0;
tmp_vel.angular.y = 0.0;
tmp_vel.angular.z = 0.0;
}
// サーバーのコールバック関数
bool Server::wheelService(my_service::Wheel::Request &req,
my_service::Wheel::Response &res)
{
ROS_INFO("Set velocity: linear=%.2f angular=%.2f",
req.target_linear_velocity, req.target_angular_velocity);
// 指令速度が最小、最大速度内かチェック
if (min_linear_velocity > req.target_linear_velocity ||
max_linear_velocity < req.target_linear_velocity) return false;
if (min_angular_velocity > req.target_angular_velocity ||
max_angular_velocity < req.target_angular_velocity) return false;
// クライアントからの速度をロボットの速度指令とする
target_vel.linear.x = req.target_linear_velocity;
target_vel.angular.z = req.target_angular_velocity;
// /odomトピックからサブスクライブした速度情報をクライアントに返す
res.current_linear_velocity = tmp_vel.linear.x;
res.current_angular_velocity = tmp_vel.angular.z;
return true;
}
// オドメトリのコールバック関数(現在速度を知る)
void Server::odomCallback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odom)
{
tmp_vel = odom->twist.twist; // 現在の速度ゲット
}
// ループ関数
void Server::loop()
{
ros::Rate loop_rate(30); // Hz
while(ros::ok()) {
// ロボットを動かすため目標速度をパブリッシュ
cmd_pub.publish(target_vel);
// コールバック関数を呼ぶ
ros::spinOnce();
// 決められた周期でループするため寝て待つ
loop_rate.sleep();
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//ROSの初期化 wheel_serverはノード名
ros::init(argc, argv, "wheel_server");
Server svr;
svr.loop();
return 0;
}
7.サービスクライアントのソースコード作成
次に仕事を依頼するのクライアントのソースコートを作成する。以下のソースコードをwheel_client.cppという名前で~/catkin_ws/src/my_service/src/wheel_client.cpp保存する。
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "my_service/Wheel.h" // 自動的に作られる
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 初期化 wheel_clientノード
ros::init(argc, argv, "wheel_client");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
// サービスクライアントの設定
ros::ServiceClient client = nh.serviceClient<my_service::Wheel>("wheel");
my_service::Wheel srv;
std::cout << "Input target linear velocity:";
std::cin >> srv.request.target_linear_velocity;
std::cout << "Input target angular velocity:";
std::cin >> srv.request.target_angular_velocity;
// サービスを呼ぶ
if (client.call(srv)) {
// 成功したらサーバーからのレスポンスを表示
ROS_INFO("Current linear_vel=%f angular_vel=%f",
(double) srv.response.current_linear_velocity,
(double) srv.response.current_angular_velocity);
}
else {
// 失敗したらエラー表示
ROS_ERROR("Faild to call service wheel");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
8.CMakeLists.txtの変更とビルド
以下をCMakeLists.txtの最後に追加する。
add_executable(wheel_server src/wheel_server.cpp)
add_dependencies(wheel_server my_service_gencpp)
target_link_libraries(wheel_server ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
add_executable(wheel_client src/wheel_client.cpp)
add_dependencies(wheel_client my_service_gencpp)
target_link_libraries(wheel_client ${catkin_LIBRARIES})
次のコマンドでビルドする。
$ cd ~/catkin_ws$ catkin build
9.実行
- 端末を開き、以下のコマンドでGazeboを起動する。
$ roslaunch ca_gazebo create_empty_world.launch
- 端末をもう1個開き、次のコマンドでサーバーを起動する。
$ rosrun my_service wheel_server
- サーバーは次のように表示される。
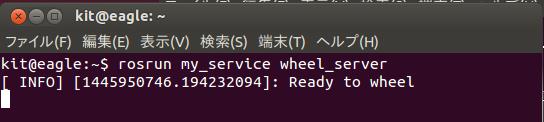
- さらに、端末を開き、次のコマンドでクライアントを起動する。
$ rosrun my_service wheel_client
- クライアントはキーボードから入力(速度指令値)をサーバーへ送る。wheel_clientを起動した端末で並進速度(linear velocty)と角速度(angular velocity)を入力してエンターキーを押すとデータがサーバーへ送られます。その速度指令値が最小、最大値の範囲外ならエラーを返す。それ以外は、シミュレータ上のロボットが動きます。
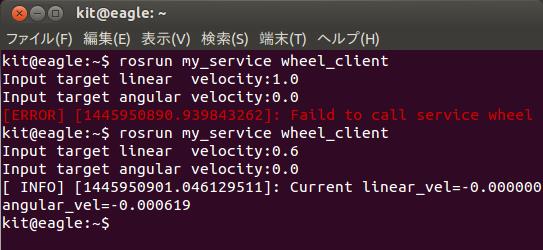
成功したら終わり。うまく動かない場合は、打ち間違えや手順に間違いがないか確認し、再度実行しましょう。
コメント