An ODE and Robotics Related Site by Kosei Demura (Profile)
I. About Me
My name is Kosei Demura. I am an adviser of the RoboCup team in Yumekobo (Factory for Dreams and Ideas) at Kanazawa Institute of Technology (KIT) in Japan, and also a professor in the Department of Robotics, KIT. More detail, please click here.
II. An ODE Related Book
I wrote an Open Dynamics Engine (ODE) related book in Japanese. Please visit the following page, you can watch simulation videos like the right sidebar (Click it !) and download sample programs such as a wheeled (differential and omnidirectional) robot, a robot arm and a 4 legged robot.
The book was translated into Korean, and published by HongReung Science Publishing Company in 2009.
III. ODE Tutorials
I wrote 15 ODE tutorials in Japanese. The following articles are mainly translated by a machine (the Google translate). So, there might be many difficulties to read them. Anyway, enjoy translated articles and sample programs. I fixed the missing links of the sample programs on January 5 in 2011.
| Lesson | Title | Abstract | Screenshot |
| 1 | Open Dynamics Engine (ODE) is an open source physics engine. Overview and features of ODE are described. |  |
|
| 2 | Install and Build | How to set up the development environment and how to install ODE. In addition, how to build your own program is also explained. |  |
| 3 | Hello Physics | Typical ODE simulation code is shown and first sample program, free fall, is explained. |  |
| 4 | Drawstuff, a simple 3D graphics library to show ODE demos, is explained. |  |
|
| 5 | A Rigid body for dynamics and a geometry for collision detection are explained. | 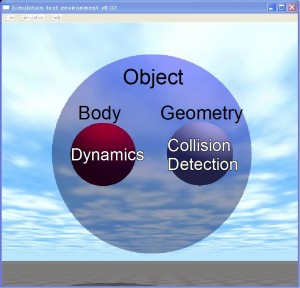 |
|
| 6 | Collision detection is explained. |  |
|
| 7 | Joint is explained that is a constraint to restrict positions and orientations of two bodies. |  |
|
| 8 | ERP (Error Reduction Parameter) and CFM (Constraint Force Mixing) are explained. These two parameters are very important for ODE. |  |
|
| 9 | Coordinate system, the unit system, a position and an orientation of rigid bodies are explained. | 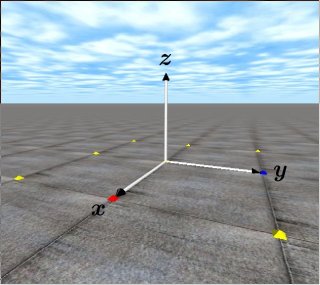 |
|
| 10 | Velocity and acceleration are explained. |  |
|
| 11 | Force and torque are explained. |  |
|
| 12 | Friction is explained. ODE friction model is an approximation of the coulomb friction. | 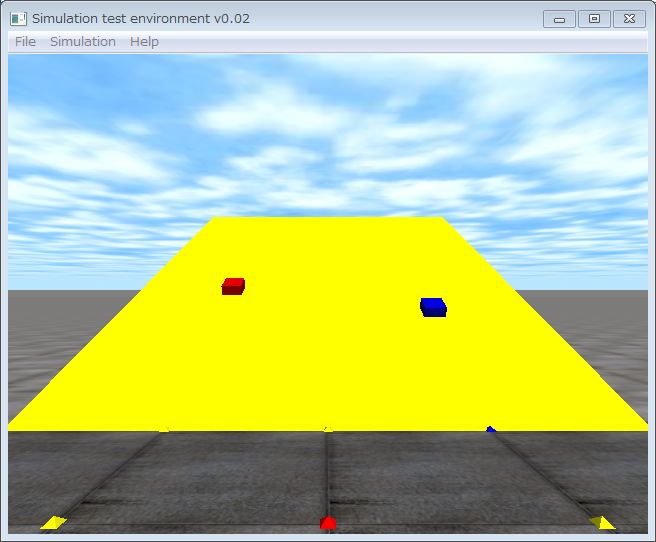 |
|
| 13 | Let’s make a robot arm using the learned knowledge of ODE. | 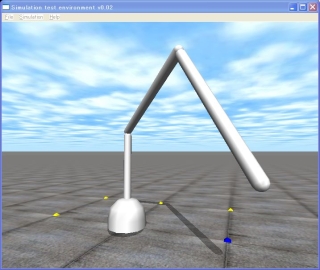 |
|
| 14 | In order to speed up the simulation, and the simulation method without using Drawstuff is explained. | 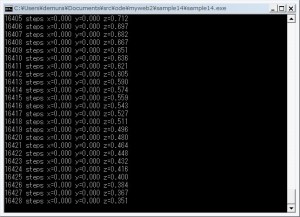 |
|
| 15 | Let’s make an interactive simulation. Learn how to use a keyboard and restart a simulation. |  |